Resolution ctDx Lung
| SNV/Indel | Fusions | CNV |
|---|---|---|
| AKT1 ALK B2M BRAF EGFR ERBB2 (HER2) FGFR2 FGFR3 KEAP1 KRAS MAP2K1 (MEK1) MET NRAS PIK3CA RET ROS1 STK11 |
ALK EGFR FGFR2 FGFR3 NTRK1 RET ROS1 |
B2M EGFR ERBB2 (HER2) FGFR1KRAS MET MYC NTRK1 PIK3CA PTEN RICTOR STK11 |
FDA Approved Therapies
| Biomarker | Therapy |
|---|---|
| exon 19 deletion exon 21 L858R |
Gilotrif® (afatinib) Tarceva® (erlotinib) Vizimpro® (dacomitinib) Iressa® (gefitinib) Tagrisso® (osimertinib) |
| EGFR S768I, L861Q, and/or G719X | Gilotrif® (afatinib) |
| ALK fusions | Alecensa® (alectinib) Alunbrig® (brigatinib) Lorbrena® (lorlatinib) Xalkori® (crizotinib) Zykadia®(ceritinib) |
| ROS1 fusions | Xalkori® (crizotinib) Zykadia®(ceritinib) Rozlytrek® (entrectinib) |
| NTRK1 fusions | Vitrakvi® (larotrectinib) Rozlytrek® (entrectinib) |
| BRAF V600E | Tafinlar® (dabrafenib) in combination with Mekinist® (trametinib) |
Clinical Utility
Our on-going, prospective study with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center has successfully generated clinical utility of the Resolution ctDx Lung assay. In the paper A Prospective Study of Circulating Tumor DNA to Guide Matched Targeted Therapy in Lung Cancers (doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djy156) the ctDx Lung assay demonstrated the following performance:
- 97% of evaluable patients who received plasma-directed therapy had a clinical and radiological response to matched targeted therapy. (34/35)
- 75% of patients not currently on therapy had a somatic mutation detected versus 42.9% for on therapy patients. Overall detection of 64.3%
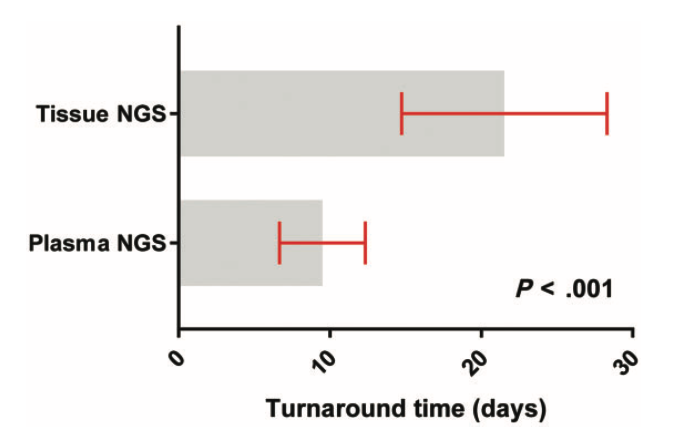
- Median turnaround time was 9 days versus 20 days for tissue NGS (p < .001).
- 45.7% of patients had an oncogenic driver alteration detected, including actionable mutations in EGFR, ALK, MET, BRAF, ROS1, and RET.
- 89.6% of patients tested positive by were concordant on tissue NGS by FDA-approved MSK-IMPACT assay (DEN170058).
- 96.1% of patients tested positive by plasma for the NCCN recognized oncogenic driver alterations (EGFR, KRAS, ALK, ROS1, RET, BRAF, MET, HER2) were concordant on tissue NGS.
- 21.9% of patients were matched to targeted therapies, including currently FDA approved therapies or therapies currently under investigation. Plasma- directed therapies included Tagrisso® (osimertinib), Iressa® (gefitinib), Tarceva® (erlotinib), Gilotrif® (afatinib), Xalkori® (crizotinib), and Alecensa® (alectinib)
Below are the spectrum and number of SNVs, Indels, CNV, and fusions detected by the ctDx Lung assay in the first 210 NSCLC patients.
Fusion Detection
Researchers at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center used the Resolution ctDx Lung assay in the study "Monitoring Therapeutic Response and Resistance: Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients With ALK+ Lung Cancer" (doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.003) to detect ALK gene fusions. The detected EML4-ALK rearrangments are plotted on the interactive graph below. The ctDx platform detects gene fusions / rearrangements without a prior knowledge of breakpoint or gene partner, resulting in the ability to not only capture canonical fusions, but also discover novel fusion partners.
Pan by dragging along the genomic coordinates. Zoom by double clicking or scroll wheel over the genomic coordinates.
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute compared the Resolution ctDx Lung Assay against Guardant Health's Guardant360® assay in the detection of the more challenging oncogenic gene fusions. The resulting paper, Sensitivity of next-generation sequencing assays detecting oncogenic fusions T in plasma cell-free DNA (doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.06.004)
Results: Of 16 patients assayed known to harbor an ALK, ROS1, or RET in tumor, G360 detected fusions in 7 cases, Resolution ctDx Lung detected fusions in 13 cases, and 3 cases were detected by neither. Of the 7 fusions detected by both assays, G360 reported lower mutant allelic fractions (AF). In cases missed by G360, tumor derived TP53 mutations were often detected confirming presence of tumor DNA. Raw sequencing data showed that inverted or out-of-frame variants were overrepresented in cases detected using ctDx Lung but not by G360.
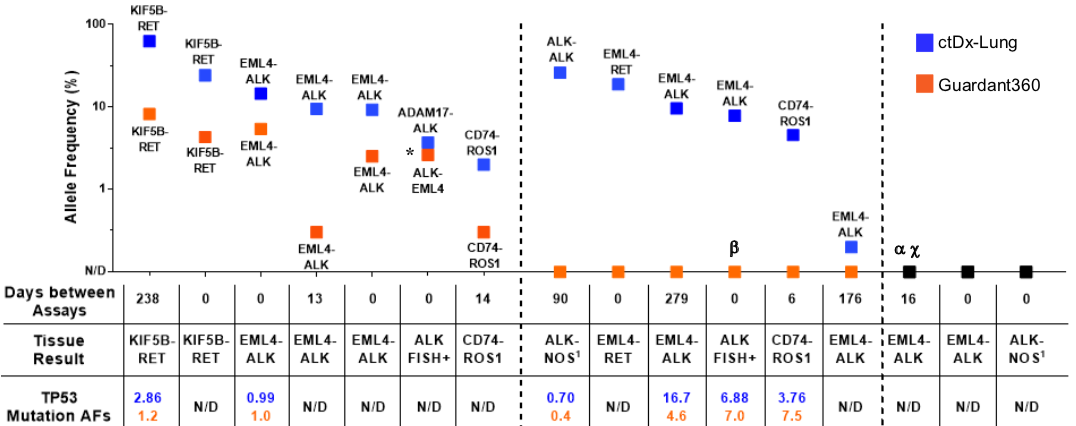
Supplee et al. Lung Cancer 2019;134:96-99